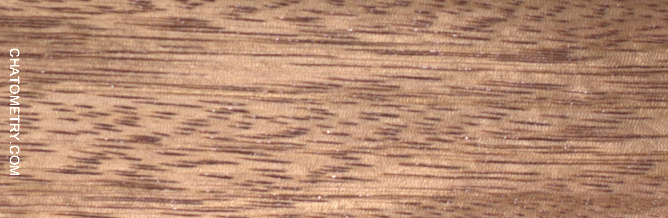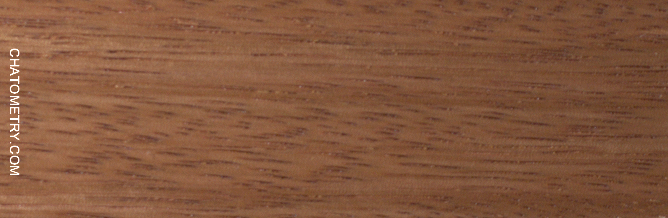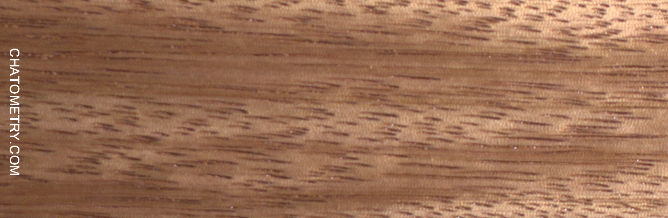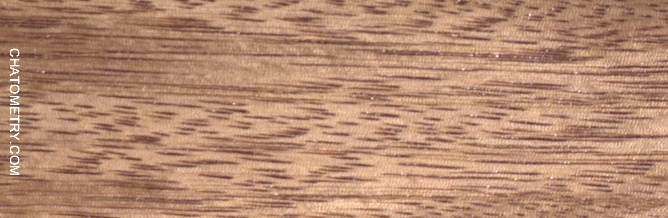
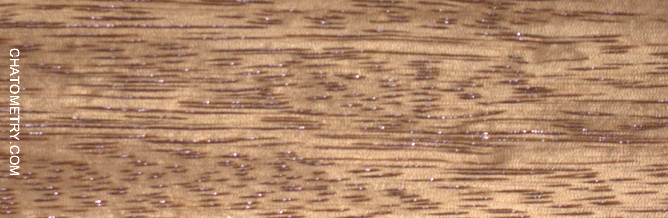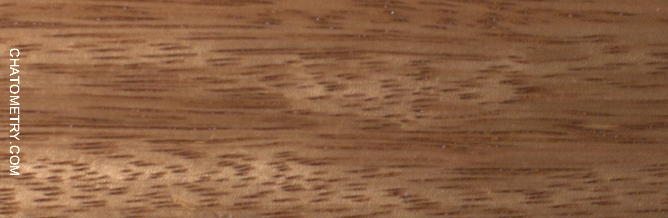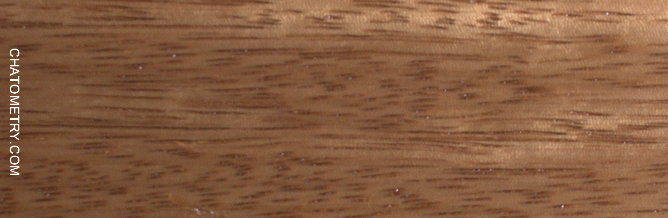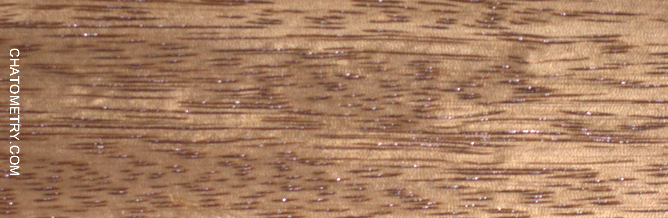
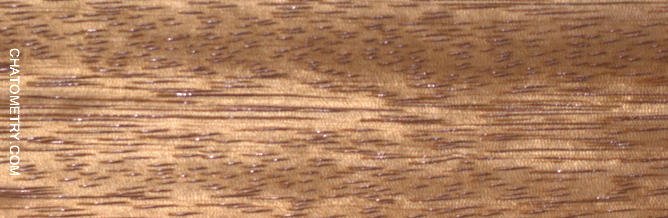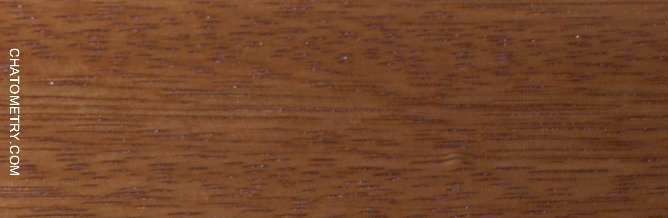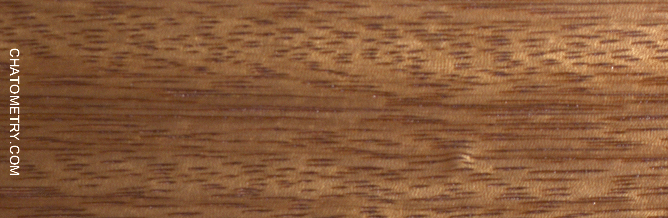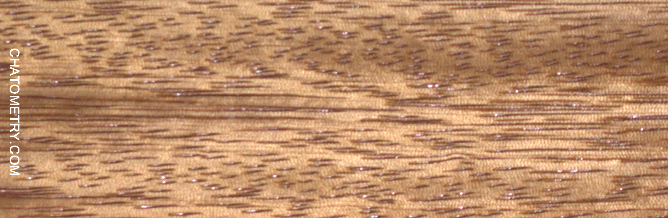
This set of tests is aimed at understanding the effect of different finishes on Niangon.
A set of 12 solid samples (from “A” to “L”) were employed; these start from very similar PZC values. All samples were sanded to 180-grit.
A special thanks goes to company Veleca for supporting us with finish samples.
We tested these finishes:
Sample A: Veleca Palkerol (water based anionic polyurethane – floor finish)
Sample B: Veleca Pinteco (acrylic emulsion – outdoor finish)
Sample C: Veleca Mobil H (water based acrylic – furniture finish)
Sample D: Veleca Nitrolux (thinner based ketone resin – classic furniture finish)
Sample E: Adler Soloplast (alkyd based finish)
Sample F: Veleca Olio per Teak (Tung oil based – exotic wood finish)
Sample G: Boiled Linseed Oil (BLO)
Sample H: Furniture restoring oil
Sample I: Nitrocellulose spray lacquer (NCL)
Sample J: Acrylic spray lacquer
Sample K: Blonde Dewaxed Shellac “Medium” (2 parts in 13 parts of Alcohol)
Sample L: Rubio Monocoat
It was concluded that:
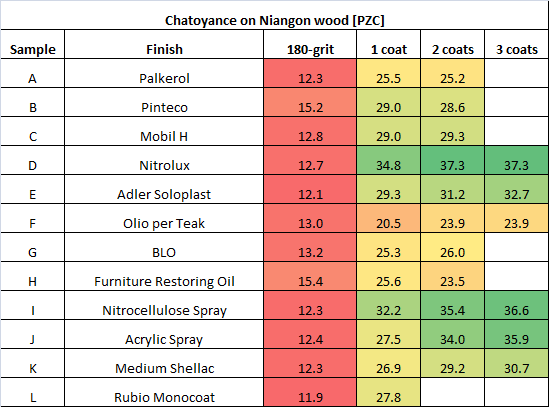
1) High chatoyance (> 35 PZC) can be achieved with Nitrolux and spray finishes, even if starting at low grit
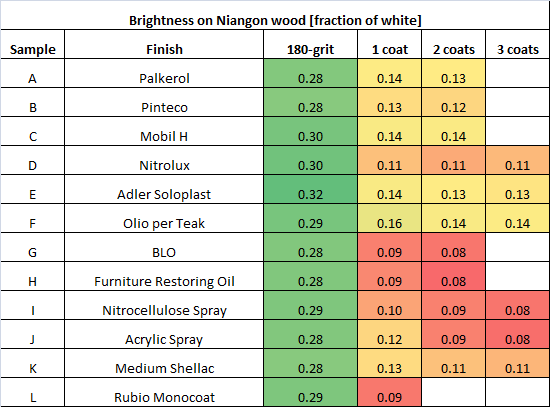
2) All these “clear” finishes significantly darken the surface
Tables below summarize the results in terms of chatoyance (PZC):
Tables below summarize the results in terms of brightness (fraction of white paper brightness):
Pictures below show the results: