What is the best finish for Curly Maple wood? Find it out here, a great woodworking resource showing tests for many different finishes.
This is a second set of tests aimed at understanding the effect of different finishes on Curly Maple.
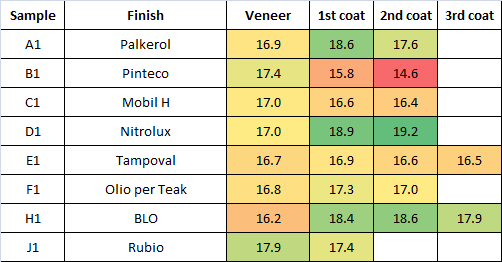
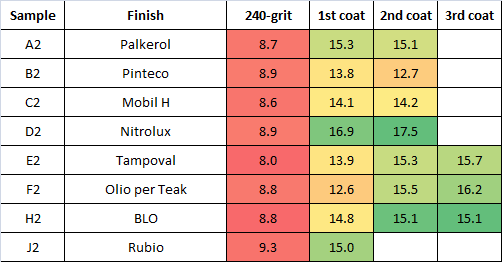
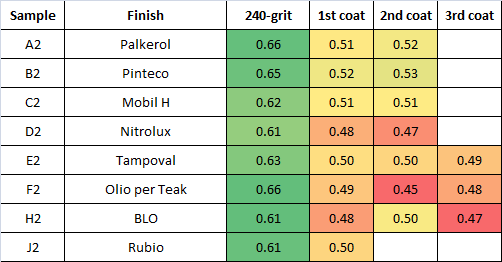
A set of 7 consecutive veneer sheets (from “A” to “H”) were employed, each split into two samples (“1” and “2”); therefore, all samples ending with “1” are just consecutive layers of the initial log and start from very similar PZC values; the same applies for samples “2”. Samples “1” were left as-received (veneer), while samples “2” were sanded to 240-grit.
A special thanks goes to company Veleca for supporting us with finish samples.
We tested these finishes:
Veleca Palkerol (water based anionic polyurethane – floor finish)
Veleca Pinteco (acrylic emulsion – outdoor finish)
Veleca Mobil H (water based acrylic – furniture finish)
Veleca Nitrolux (thinner based ketone resin – classic furniture finish)
Veleca Tampoval (blonde dewaxed shellac – antique furniture finish)
Veleca Olio per Teak (Tung oil based – exotic wood finish)
Boiled Linseed Oil (BLO)
Rubio Monocoat
It was concluded that:
1) chatoyance is increased by all of these clear coats
2) Nitrolux, Tampoval, and Teak Oil provide the best results, even better than BLO
3) Some of these “clear” finishes significantly darken the surface
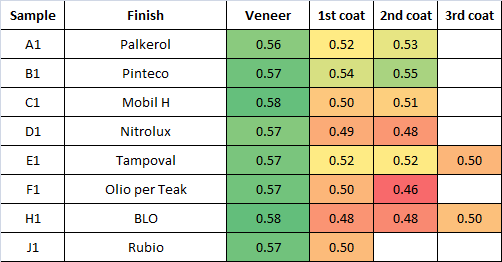
4) Interestingly, very similar final brightness is obtained from sanded and veneer-as-received samples, even if sanded sample start with a higher brightness
Tables below summarize the results in terms of chatoyance (PZC):
Tables below summarize the results in terms of brightness (fraction of white paper brightness):
Pictures below show the results:



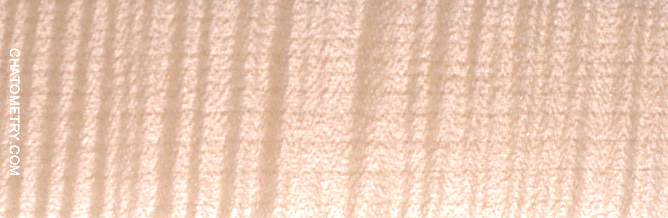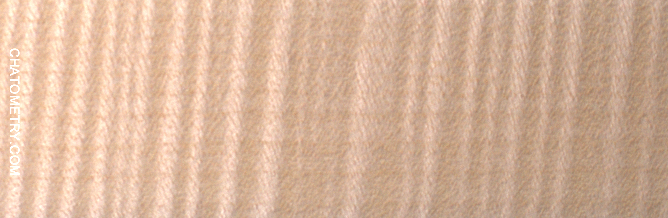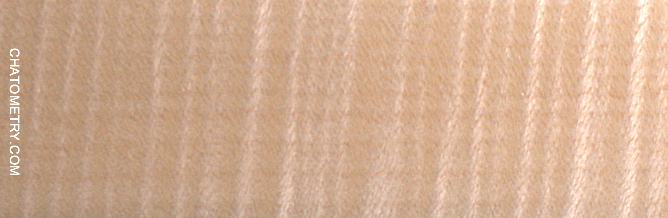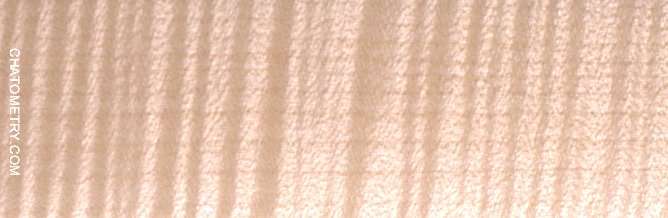





Want to know more? Get Woodworker’s Guide to Chatoyance!

Available on Amazon in 12 countries – just click on your flag below…
… and enjoy the read!